
-1.png)
Sensors
From Sensor Research and Development
to Implementation in Detectors








Riken Keiki draws on 85 years of accumulated expertise to offer a lineup of more than 10 detection principles and over 1,400 in-house developed sensors. To meet the needs of various applications and fulfill the requirements of each user, we present our high-quality, high-performance sensors, proudly made in Japan and developed in-house.
At the heart of any gas detector is its sensor. While many competitors outsource the design and manufacturing of the sensors used in their gas detectors, here at Riken Keiki we design, manufacture and supply all sensors used in our gas detectors in house, testament to our unwavering commitment to ensuring workplace safety. Only sensors proven to meet our exacting quality and performance standards which successfully pass several rounds of field testing make it into our products. We have two factories located in Japan (our Kasukabe Production Center in Saitama Prefecture and our Hakodate Factory) which meet ISO 9001 quality standards, manufacturing about one million sensors each year.

① New Ceramic Sensor
This sensor uses an ultra-atomized oxidant catalyst (a new ceramic) to detect gas in a wide range of concentrations from a low level (ppm) to the Lower Explosion Limit (LEL). This pioneering new sensor was designed by Riken Keiki specifically for the detection of combustible gases.

① New Ceramic Sensor

② Optical Interferometric Sensor
This sensor detects changes in the refractive index of gases. It works by generating conversion formulas based on the unique refractive index of each gas to determine its concentration. It operates without the use of chemical reactions, delivering highly sensitive gas readings without deteriorating over time, even in environments where gases are constantly present. Its fast response time makes it suitable for monitoring system sensors.

② Optical Interferometric Sensor
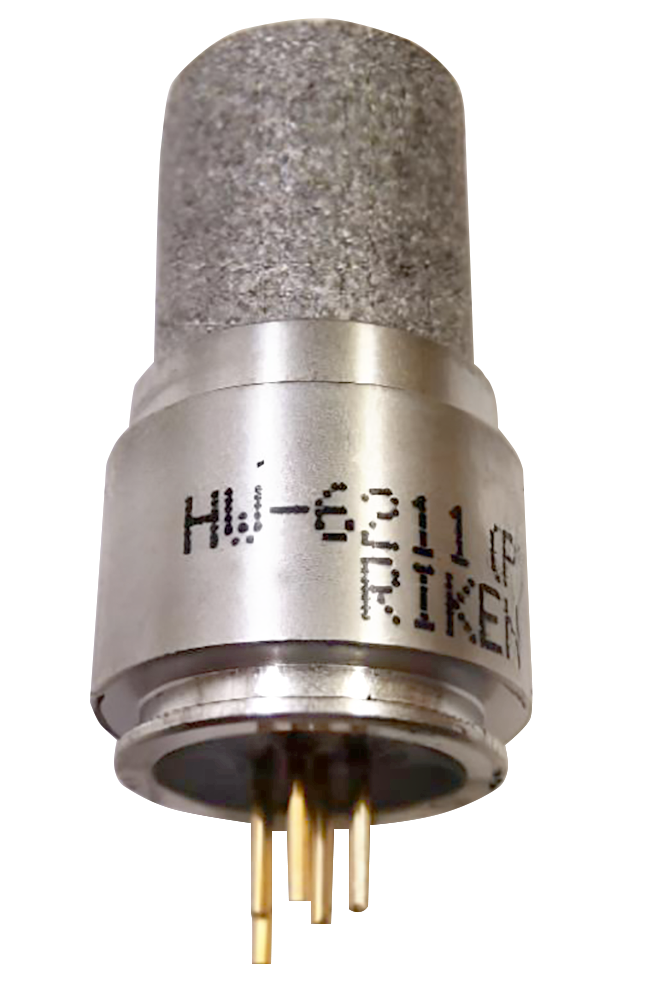

③ Catalytic Combustion Method
This sensor uses the heat generated upon combustion as combustible gases come into contact with an oxidation catalyst. It is the most widely used sensor specifically for combustible gases worldwide.

③ Catalytic Combustion Method

④ Semiconductor Sensor
This sensor detects gas concentration by measuring changes in resistance when a metal oxide semiconductor comes into contact with the target gas. It is a versatile gas sensor capable of detecting a wide range of gases, from toxic to combustible.

④ Semiconductor Sensor

⑤ Hot Wire Type Semiconductor Sensor
This sensor detects gas concentration by measuring changes in resistance when a metal oxide semiconductor comes into contact with the target gas. It is a highly sensitive sensor designed for detecting low concentrations of gases.

⑤ Hot Wire Type Semiconductor Sensor
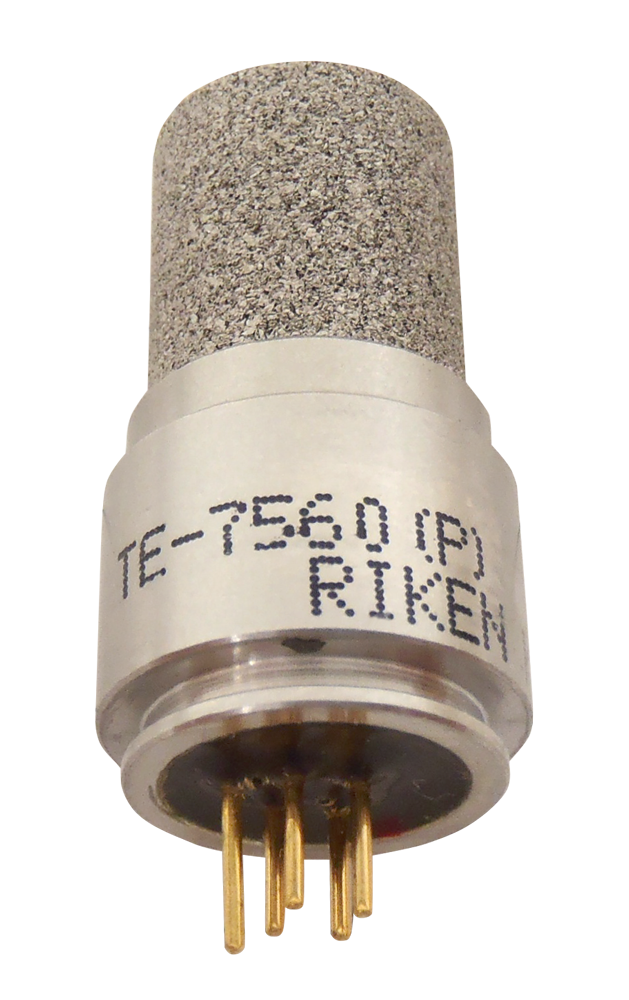

⑥ Thermal Conductivity Sensor
This sensor detects gas concentration by measuring changes in thermal conductivity caused by the target gas. It is a proven and reliable combustible gas sensor, specifically suitable for detecting high gas concentrations.

⑥ Thermal Conductivity Sensor

⑦ Potentiostatic Electrolytic Sensor
This sensor electrolyzes the target gas on an electrode maintained at a constant potential and detects the resulting current to determine gas concentration. It is one of the most effective sensors for detecting toxic gases and can selectively detect specific gases by adjusting the electrode potential.

⑦ Potentiostatic Electrolytic Sensor
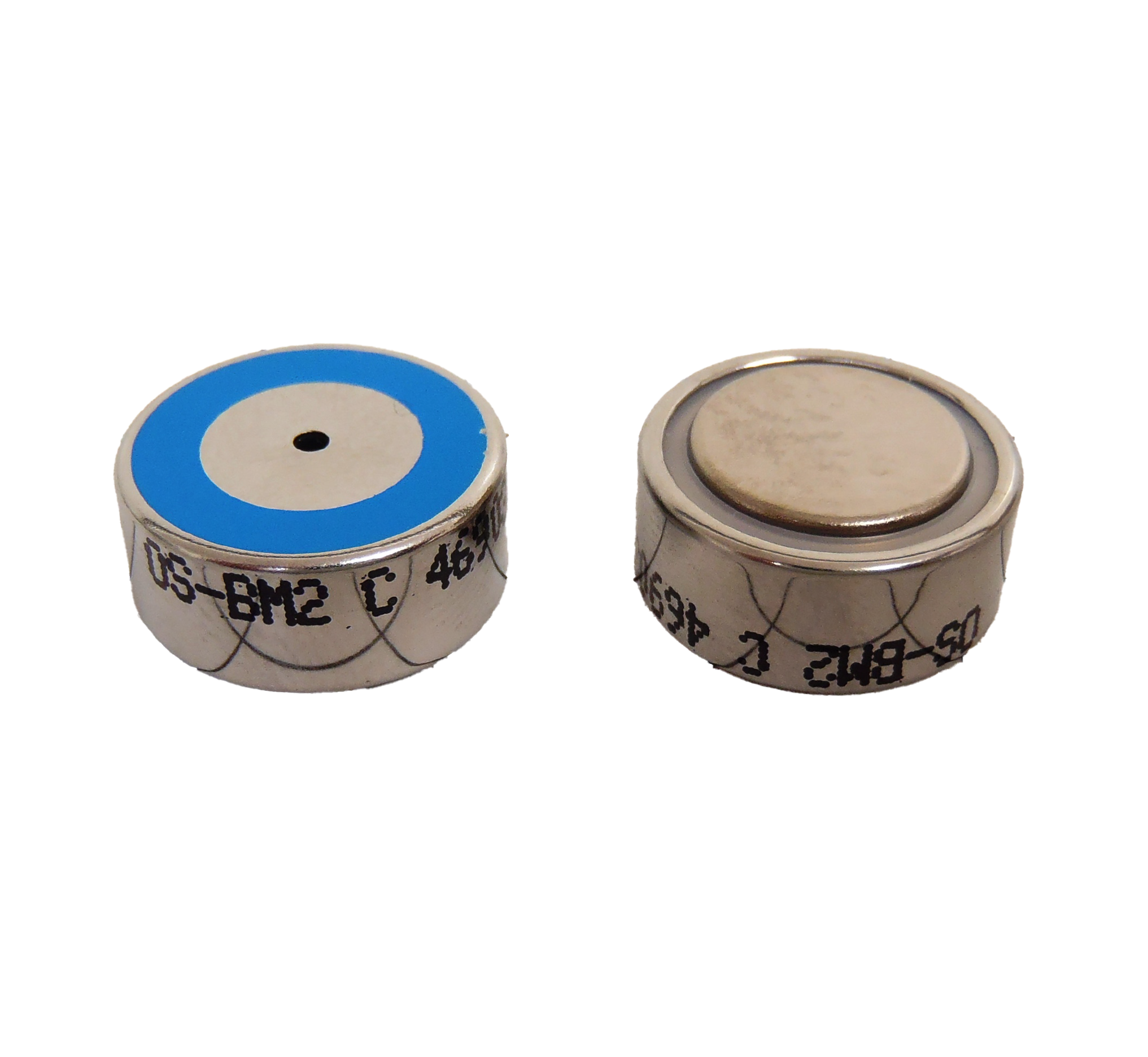

⑧ Membrane Type Galvanic Cell Sensor
This simple, time-tested oxygen sensor applies the basic principles of a battery. It requires no external power source and provides excellent long-term stability.

⑧ Membrane Type Galvanic Cell Sensor
⑨ Non-Dispersive Infrared Sensor
This sensor detects gas concentration by utilizing the fact that many gases absorb infrared radiation. Infrared light is directed into a measurement cell, and the sensor detects changes in the light caused by absorption from the target gas. It detects infrared light within a specific wavelength range without separating it by wavelength. With excellent gas selectivity, it can measure the concentration of a specific gas component even in the presence of multiple gases.

⑨ Non-Dispersive Infrared Sensor

⑩ Membrane-Separated Electrode Sensor
Based on the potentiostatic electrolytic principle, this sensor features a structure that completely separates the gas-permeable membrane from the working electrode. It is a toxic gas sensor that offers excellent selectivity.

⑩ Membrane-Separated Electrode Sensor

⑪ Chemical Tape Sensor
The target gas passes through or diffuses into a cellulose tape impregnated with a color-forming reagent. As the gas reacts with the reagent, a visible color appears on the tape. The sensor electrically measures the intensity of the reflected light from this color change, enabling quantitative detection of extremely low concentrations of toxic gases.

⑪ Chemical Tape Sensor
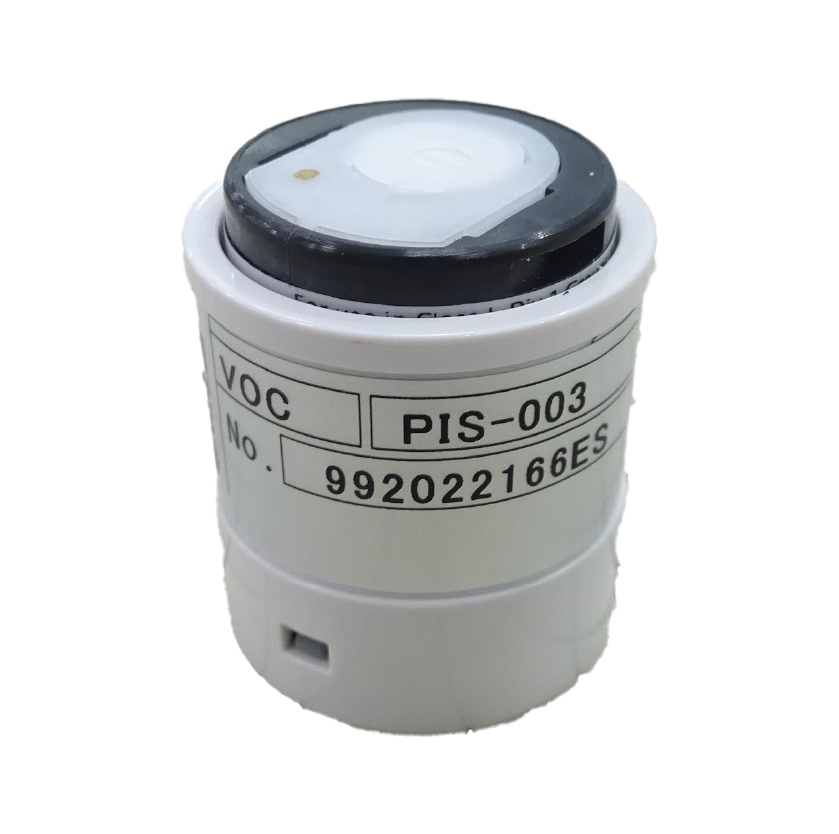

⑫ Photoionization Sensor
This sensor ionizes the target gas by irradiating it with ultraviolet light and measures the resulting ion current to determine gas concentration. It is capable of detecting a wide range of gases, both organic and inorganic, and is commonly used to measure volatile organic compounds (VOCs) at levels from ppb to ppm.

⑫ Photoionization Sensor

⑬ Pyrolysis Particle Sensor
This sensor heats the target gas, generating oxide particles that are measured by a particle sensor. It offers excellent long-term stability, strong resistance to interference, and fast response time. The particle sensor operates on the same principle as an ionization-type smoke detector that uses radiation.

⑬ Pyrolysis Particle Sensor



See Our Solutions in Action!
